The gynecomastia pinch test is a simple diagnostic tool used to quickly and easily ascertain if a patient has this embarrassing (yet benign) condition. Though it can be performed at home, it’s usually best to let a medical professional perform the diagnosis.
Read on to learn more about the gynecomastia pinch test and how it is performed.
What Causes Gynecomastia?
The defining characteristic of gynecomastia is the enlargement of male breasts, and is usually caused by an imbalance between the patient’s levels of estrogen and testosterone. This imbalance can be caused by many things:
- Adolescence: the hormonal changes brought about by puberty can cause temporary gynecomastia. The problem generally resolves itself within six months to two years.
- Infancy: a male baby may suffer short-term gynecomastia as a result of the remaining estrogen from his mother still in his system. The condition, as with adolescent gynecomastia, resolves itself.
- Medications: Many kinds of medication including anti-androgens, HIV treatments, anabolic steroids, anti-anxiety and anti-psychotic meds, chemotherapy, ulcer medication, heart medication and certain antibiotics.
- Substance Abuse: alcohol, methamphetamine, marijuana, heroin and methadone abuse may all cause gynecomastia.
- Underlying Health Conditions: several health conditions can cause or exacerbate gynecomastia. These include hypogonadism, aging, certain cancers, hyperthyroidism, kidney/liver failure, cirrhosis, and malnutrition/starvation.
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
The symptoms of gynecomastia are as follows:
- Swollen breast tissue
- Tenderness in the breast area
- Pain in the breast area (particularly prevalent in adolescents)
- Sensitive nipples, especially with regards to chafing against clothing
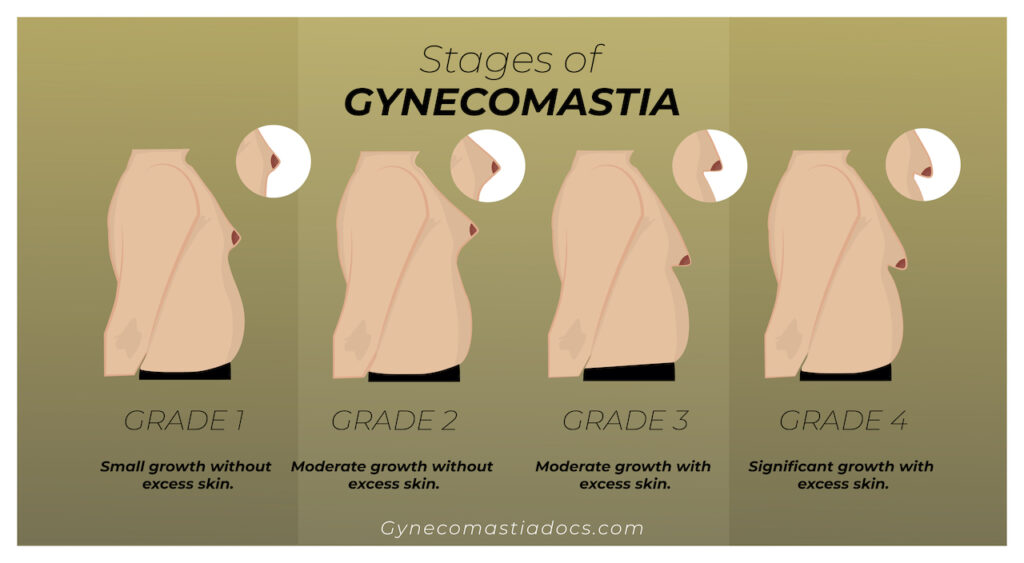
What Are the 4 Grades of Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia has four distinct stages (feel free to learn more about these Gynecomastia Grades).
Stage 1: Small Breast Enlargement without Excess Skin
Considered minor, this level of gynecomastia involves a small amount of excess breast tissue and is generally not visible through clothing. As it can be psychologically distressing, however, treatment (including surgery) is often prescribed.
Stage 2: Moderate Breast Enlargement without Excess Skin
This stage is characterized by moderate breast growth that expands across the chest. Breasts are noticeable through light clothing, such as T-shirts. This stage can cause significant psychological upset, and so recourse to surgery is often made.
Stage 3: Moderate Breast Enlargement with Excess Skin
Significant breast development can be seen at this stage. The breast tissue swells beyond the confines of the chest and is very noticeable, even when fully clothed. At this point, surgery is the only realistic option for reduction of the breasts.
Stage 4: Significant Breast Enlargement with Excess Skin
There is a substantial enlargement of breasts at this stage; the breasts are very obvious, even when heavily clothed, and can often mimic female breasts. As with stage 3, the only realistic treatment at this point is surgery.
Gynecomastia vs. Pseudogynecomastia: What’s the Difference?
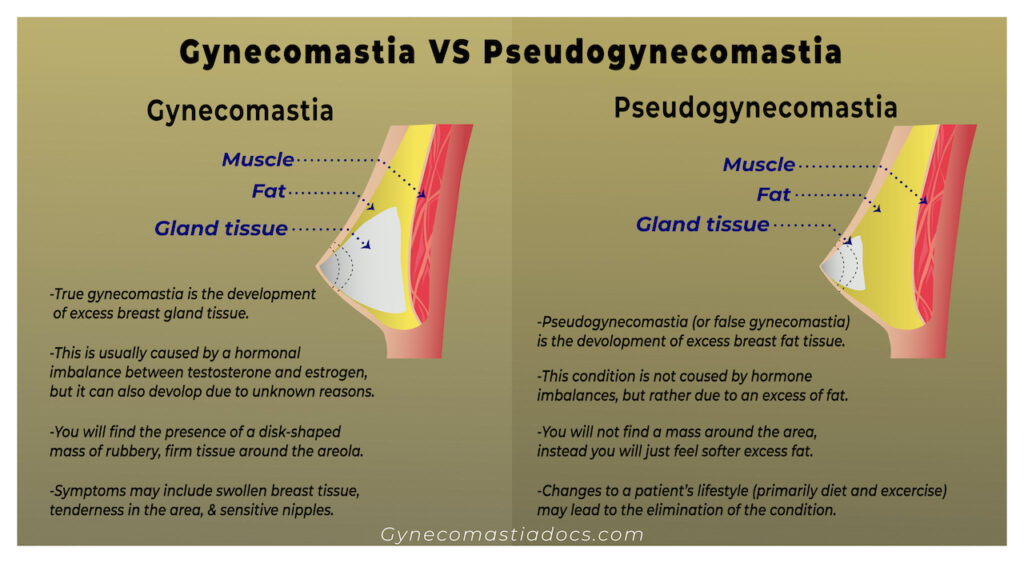
It can be quite easy to assume that enlarged breasts in a man are caused by gynecomastia, but it’s a mistake to do so. Without a proper medical diagnosis, it’s impossible to say for sure if you’re dealing with actual gynecomastia, or a similar condition called ‘pseudogynecomastia’.
What is Pseudogynecomastia?
Pseudogynecomastia is characterized by an excess of adipose (fat) tissue around and under the nipples. This condition is not caused by hormone imbalances, but simply due to an excess of fat.
Note that it is quite common for patients with gynecomastia to have both excess breast gland tissue and excess breast fat tissue. In these types of cases, both will be removed during a surgical procedure.
Because pseudogynecomastia has a relatively simple cause, it’s consequently more identifiable to treat. Changes to a patient’s lifestyle (primarily diet and exercise) can lead to the elimination of the condition.
How is Gynecomastia Diagnosed?
Because gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia can resemble each other so closely, it’s often necessary for a physician – preferably a surgeon who specializes in gynecomastia – to diagnose the condition.
In order to diagnose gynecomastia, a doctor will need to see you in person and physically examine the area.
It’s possible that the doctor will suspect a case of pseudogynecomastia, rather than the genuine condition. If this is the case, they may well administer something called the ‘pinch test’.
What is the Gynecomastia Pinch Test?
The primary difference between gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia is that the former is characterized by the presence of excess breast gland tissue, while the latter is the excess of breast fat tissue.
A physician looking to distinguish between the two will therefore use the ‘pinch test’, which can quickly and accurately ascertain the presence of excess breast gland tissue (or lack thereof).
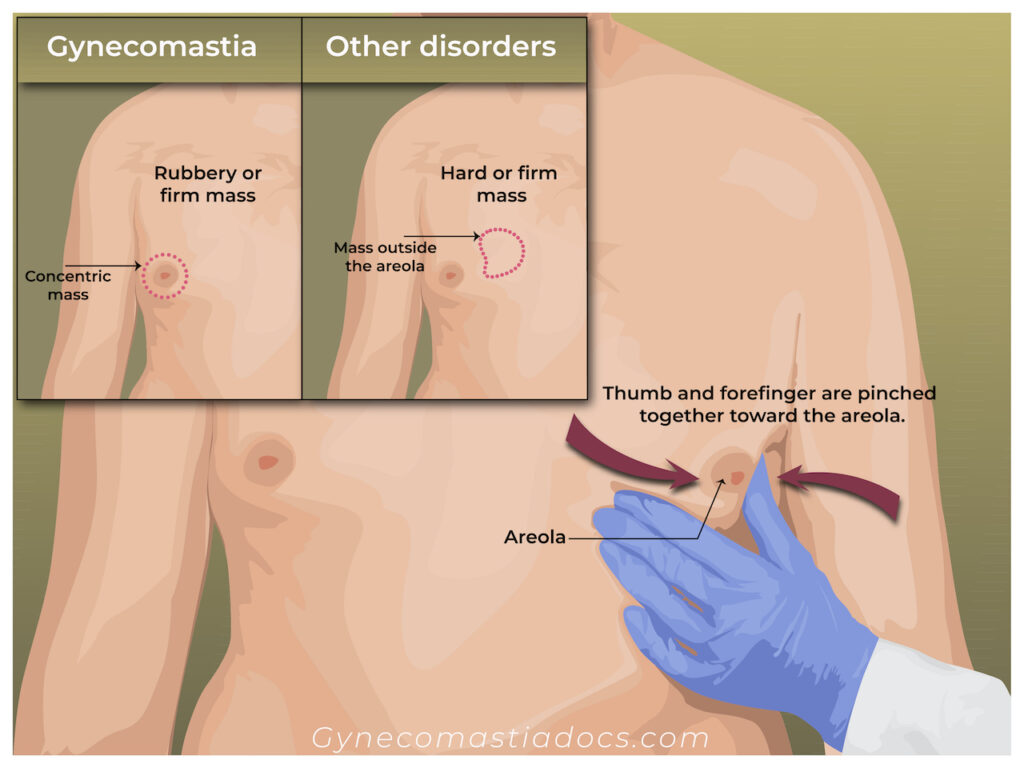
Diagnosing Gynecomastia with the Gynecomastia Pinch Test
In order to diagnose gynecomastia with the gynecomastia pinch test, a doctor will ask the patient to lie on their back and expose their chest. Using their thumb and forefinger, the doctor will physically examine the area under and around the patient’s nipple.
In the case of actual gynecomastia, the doctor will find a disk-shaped mass of rubbery, firm tissue in the area. This tissue is breast gland tissue, and indicates a case of true gynecomastia.
If the doctor merely finds spongy, soft tissue in the area, then it can be concluded that only fat tissue is found. In this instance, it’s highly likely that the patient is suffering from pseudogynecomastia.
As part of the test, it’s also possible that the physician will pinch the patient’s nipple firmly, in order to assess the level of tenderness and whether or not there is an undue level of pain. If the nipple is overly tender or painful, the doctor may take this as further evidence in favor of a positive diagnosis of gynecomastia.
Can You Do a Pinch Test on Yourself?
It’s certainly possible to examine your own chest/breast, and the feel of gynecomastia is quite distinct – a hard, fibrous disk of solid tissue below and around the nipple – but this is hardly a definitive diagnosis.
It’s therefore important to get checked out by a doctor if you suspect gynecomastia. Not only can the doctor confirm or allay your suspicions, but they also can engage in differential diagnoses to eliminate other potential conditions.
Does Gynecomastia Hurt When Pressed?
The lump that accompanies gynecomastia can hurt when pressed, but this is not always the case.
Does Gynecomastia Feel Like a Lump?
As mentioned above, gynecomastia is indeed a disk-shaped lump found below the nipple. It may move around within the breast tissue easily when pushed or probed.
How Big is a Gynecomastia Lump?
A gynecomastia lump can be in the range of 0.5cm in diameter; it is commonly described as ‘button-shaped’, and so is not generally very large. However, each case of gyno may be different.
What is the Treatment for Gynecomastia?
Once a definitive diagnosis has been made, it’s time to look at gyno treatment options. The options vary depending on the age of the patient, medical history, and the severity of the gynecomastia.
Infant/Adolescent Gynecomastia
Generally speaking, no treatment is needed for either of these instances of gynecomastia. Both will most likely resolve themselves in a matter of months (for the former) or a year or two (for the latter).
Off-Label Medication
Some medications that are commonly used for the treatment of breast cancer can be used to alleviate the symptoms of gynecomastia. Tamoxifen and Raloxifene, though not explicitly gynecomastia medications, can both be of help to sufferers of the condition.
Aromatase inhibitors – that is to say, drugs that prevent the production of aromatase, which converts testosterone into estrogen – can also be of use. One such inhibitor is Arimidex.
Be sure to consult a doctor before moving forward with any type of medication.
Treatment of Underlying Conditions
As previously mentioned, many underlying conditions may cause or exacerbate gynecomastia. It is quite often the case, that if that condition is effectively treated, the symptoms of gynecomastia may also be alleviated or eliminated entirely.
Drug/Alcohol Abstinence
Though it will not help in the later stages of gynecomastia, drug or alcohol abuse can increase your chances of developing gynecomastia. It can also exacerbate an existing condition, making a previously concealable case into one that can be noticed even through clothing.
For these reasons, it’s a good idea to refrain from drinking to excess. Drugs such as cannabis or methamphetamine should also be avoided altogether.
Diet
As with alcohol and drugs, diet cannot reverse a case of gynecomastia that has already become symptomatic – but it can alleviate it. Carefully managing your gyno diet can also prevent it from manifesting in the first place.
Foods that are rich in zinc and healthy fat can boost testosterone production, thereby avoiding the hormonal imbalance that causes gynecomastia in the first place. Such foods include eggs, olive/coconut oil, lean meats and certain seafood, such as oysters.
If already suffering from gynecomastia and experiencing pain or tenderness in the breasts, foods with anti-inflammatory properties can be beneficial. Consider incorporating salmon, tuna, unprocessed fruit juices, berries and leafy greens into your diet.
Surgery
Though many patients might prefer to get rid of gynecomastia without surgery, the fact of the matter is that it is usually the only realistic option after stage 1 gynecomastia.
There are two surgical options for gynecomastia:
Liposuction (Fat Removal)
Removal of breast fat via cannulae inserted into small incisions. However, this surgery will not solve the issue of excess breast gland tissue.
Breast Gland Tissue Removal
This surgery involves the removal of the excess breast gland tissue. If you opt for surgery, you will have the highest chance of solving your gyno issues.
Combination
The most involved surgery but also likely the best for esthetic purposes, is both liposuction and breast gland removal. This will take care of both excess breast fat and gland tissue.
Gynecomastia Pinch Test Recap
Though it can be tempting to self-diagnose a case of gynecomastia – particularly with something that seems as simple and straightforward as the gynecomastia pinch test – it is important to go see a doctor.
Any medical condition should be diagnosed by a trained professional, who has the knowledge and experience to discount similar conditions and provide you with the best medical advice possible.
